Are you curious about the state of AI in Malaysia?
In 2023, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has taken storm in the media.
It began with the poster boy ChatGPT, MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and many other generative AI applications.
So, how is AI doing in Malaysia after one year?
Do people trust it? Are companies ready for it? What are the government’s plans to push AI forward?
Let’s find out.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI in short, is a branch of computer science. Its goal is to develop machines that can perform tasks that typically need humans.
AI equips computers with the ability to think and learn. AI uses machine learning algorithms to learn from data.
But AI is not just about following instructions, it’s about making decisions and solving problems, like how humans do.
In general, there are two main types of AI:
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI is like the super-smart computer you always see in the movie.
They can understand, learn, play, and do anything like a normal human.
Remember Jarvis? Tony Stark’s personal AI in Iron Man 3.
JARVIS actually stands for Just A Rather Very Intelligent System. What a name.
But it is intelligent.
JARVIS speaks with a calm voice, it’s witty, it’s able to understand and perform complex instructions.
It can also control Tony Stark’s home, manage the iron man suit, and even assist in research and analysis.
AGI is like the jack-of-all-trades in the AI world.
With all th excitement about AI going on these days, you must be thinking we are not far from that in our real life, right?
But sorry to say that. According to Professor Andrew Ng (founder of Deeplearning.AI), we are still at least 40-50 years away from AGI.
But, don’t get too devastated just yet. At least we have ANI.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
99% of the AI systems we see today is ANI.
These are computers that are really good at one area.
For example, a chess-playing AI can beat champions, but it can’t even draw a simple picture.
Or, a chatbot cannot even perform simple maths.
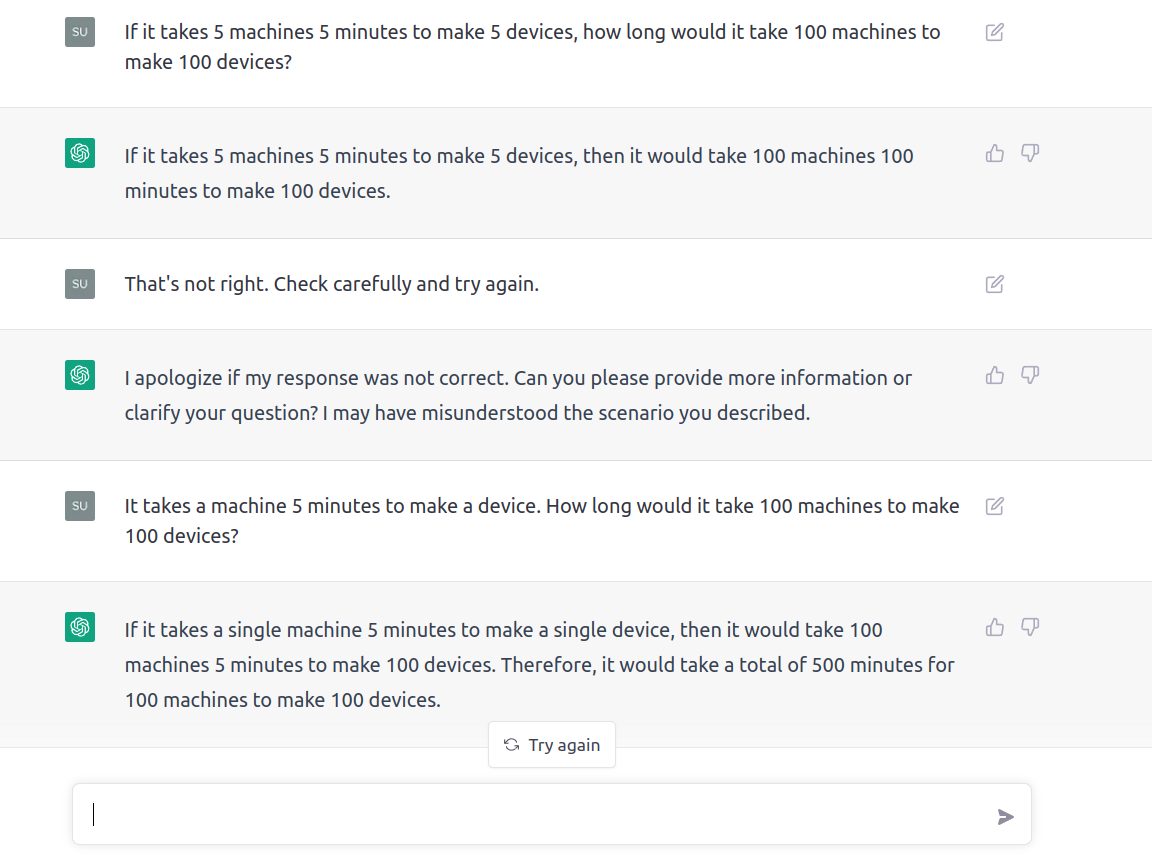
The first version of ChatGPT failed to understand even a simple math question.
This is due to the fact that ANI systems are trained on a huge amount of data but on a specific type of data. They learn how to make decisions and perform actions solely based on the data.
Therefore, ANI can perform the tasks they are designed to perform (e.g., driving cars, detecting spam, drawing images, playing chess) very well but cannot adapt to new tasks.
It’s like being the best in the world at one subject in school but not knowing much about anything else.
| Feature | ANI | AGI |
| Task | Can perform a single task or a narrow set of related tasks | Can perform any task that a human can |
| Generality | Not general | General |
| Training data | Large dataset of data specific to the task | No specific dataset required |
| Generalization | Cannot generalize to new tasks or situations | Can generalize to new tasks and situations |
ANI vs. AGI at a quick glance.
Current AI Landscape in Malaysia
2023 has been a thrilling year for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Malaysia.
Malaysian government has been proactively pushing for AI in government services. Federal government and state government also uses AI in sentencing.
We experience rapid growth in this field, more companies are willing to invest and explore, and government are actively supporting AI initiatives.
Government Initiatives
MOSTI (Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation), first launched the Malaysia AI Roadmap to outline how the country’s AI capabilities can be strengthened within 2021 until 2025.
The roadmap is to serve as a guideline to create an AI innovation ecosystem, and using AI as a critical driver that helps the country to stay productive and maintain competitive edge.
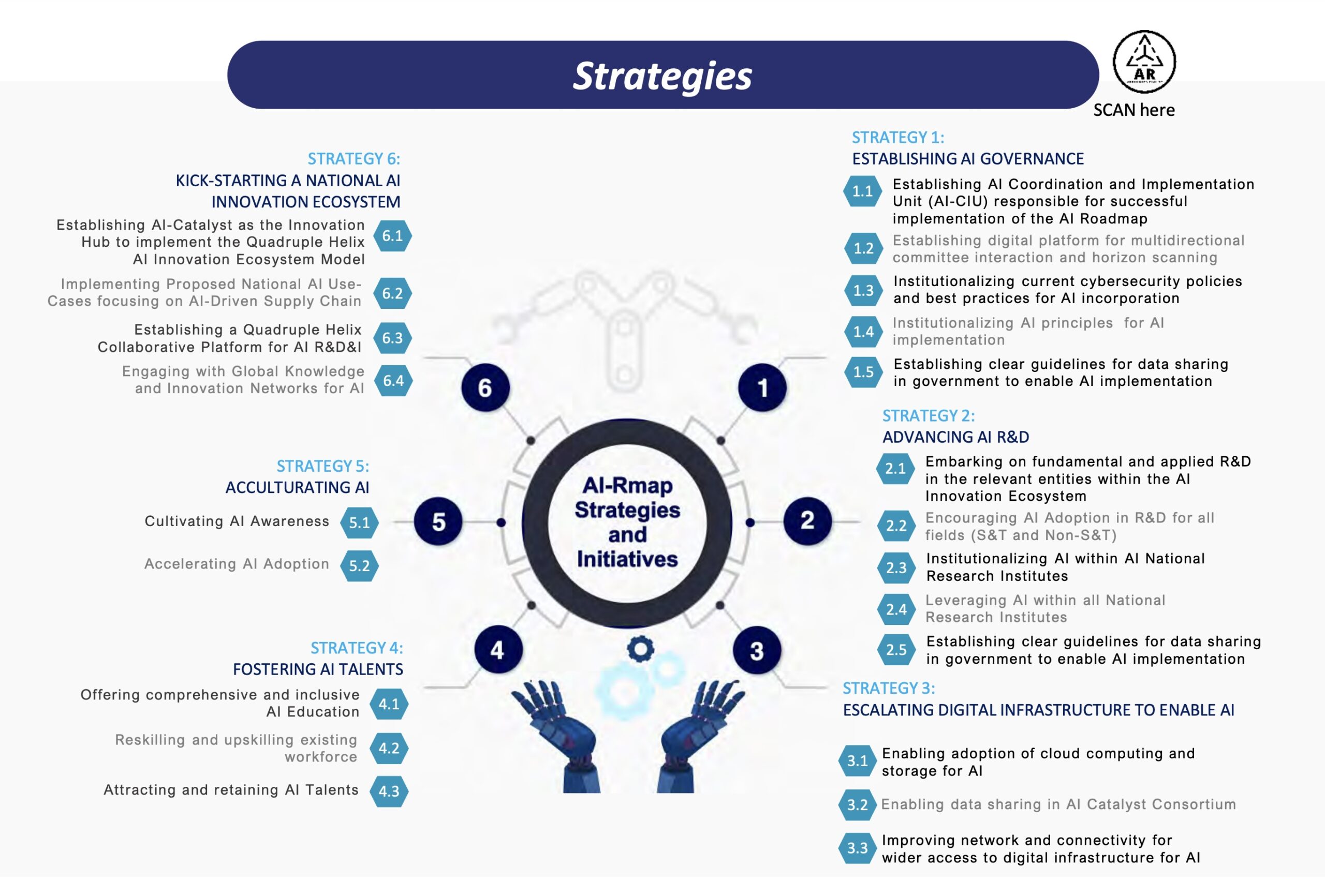
The AI-RMap has six key pillars:
- Establishing AI Governance: This pillar aims to develop a robust AI governance framework to ensure that AI is used ethically and responsibly.
- Advancing AI R&D: Embarking on fundamental and applied R&D in the relevant within AI ecosystem.
- Escalating AI Digital Infrastructure: This pillar aims to use AI to improve productivity and economic growth across all sectors of the economy.
- Fostering AI Talents: This pillar aims to use AI to solve social challenges, such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Acculturating AI: This pillar aims to create a thriving AI innovation ecosystem in Malaysia.
- Kickstarting an AI Ecosystem: This pillar aims to create a thriving AI innovation ecosystem in Malaysia.
You may also compare it to the National AI Initiative framework by the USA here.
Universities, R&D, and Education
The Budget 2024 allocated a initial fund of RM 20 million, to setup the first AI faculty in Malaysia at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM).
It is believed that it will be a great addition to the existing Center for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIRO).
University programs
An artificial intelligence (AI) degree at a university is vital when it comes to producing talents to meet the growth of AI across industries.
A good AI degree should equip students with technical skills focuses on topics like machine learning, human-AI interaction, robotics, computer vision, and natural language processing (NLP).
The degree should also cover how to develop ethical AI systems, addressing biases, and building AI models that we can explain and deploy to production.
An AI graduate need not to be working in the IT or tech industry. The interdisciplinary nature of AI degrees allows students to complement their technical expertise with skills in areas like psychology, cognitive science, linguistics, and philosophy.
Graduates with AI degrees are prepared to fill these jobs of the future as data scientists, machine learning engineers, AI consultants, roboticists, and other emerging roles.
Or, they can pursue a higher degree like Masters by research or a PhD, to continue their research journey.
Here are some of the key university AI degree programs in Malaysia.
AI Related Startups in Malaysia
Tapway
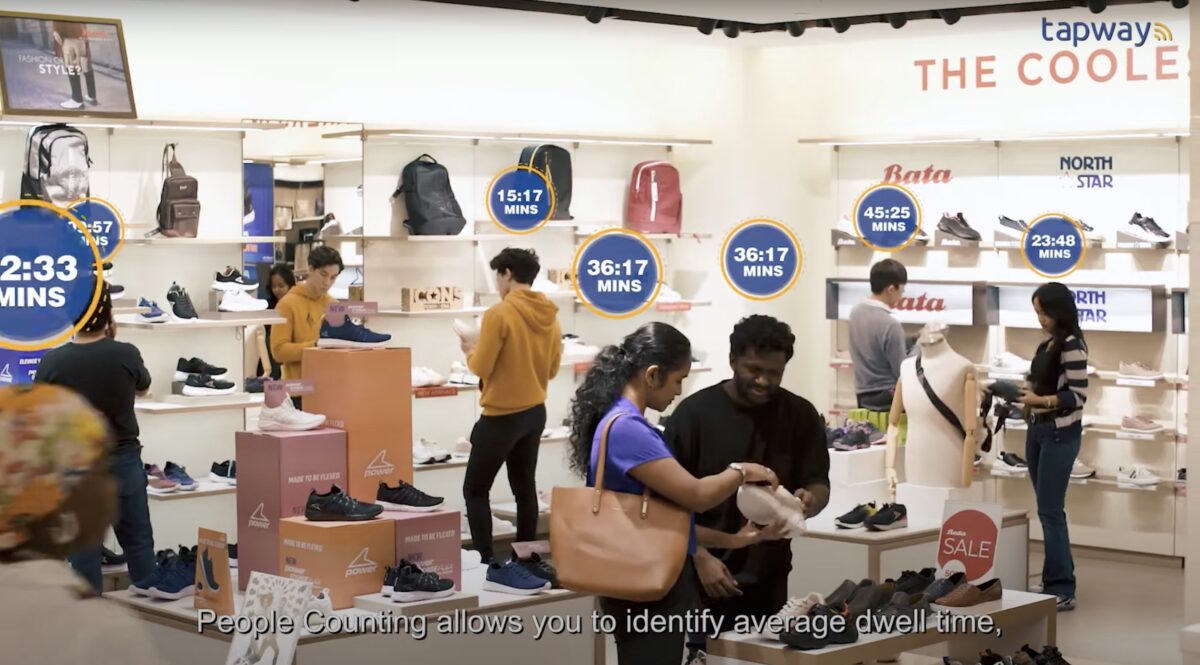

Tapway is a company specializes in combining machine learning, computer vision, and IoT to create intelligence systems.
Their primary focus is on developing AI solutions for smart buildings, retails, and manufacturing.
Their key AI technologies is able to classify objects in images and videos. It can also track people, watching how they move around as it happens.
These AI are used for footfall tracking in retail stores. They can count visitors and build an anonymous profile for each.
It’s like Google Analytics, but for physical shops.
Katsana
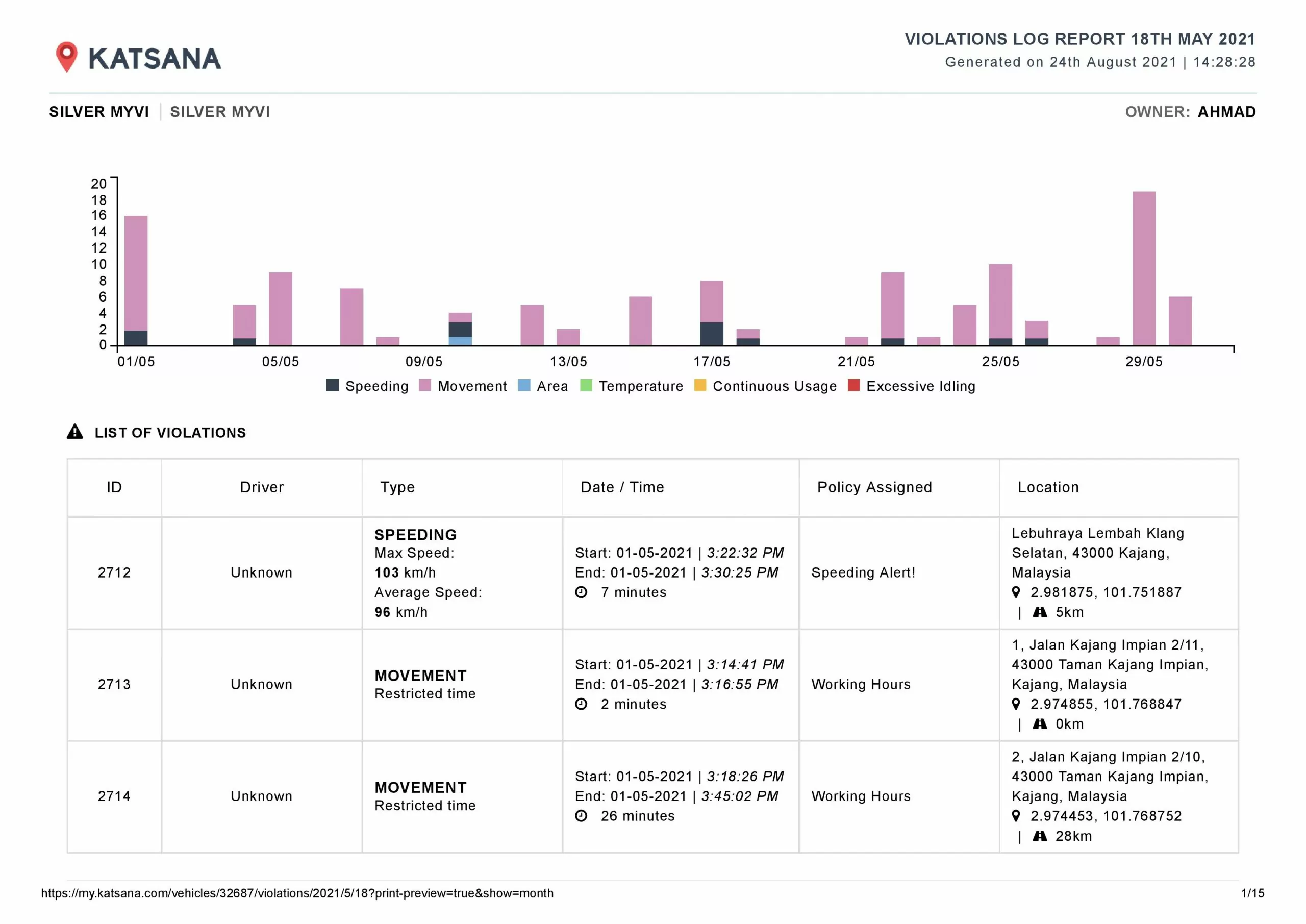
Katsana is a company that uses advanced telematics to manage fleets and industrial operations.
For fleet management, they have an AI fleet tracking platform that combines GPS data and drivers behaviours.
This help to find the best routes, saving fuels, and boost driver safety.
They also use IoT devices and sensors to gather real-time driving data, to facilitate remote operation monitoring. This will automate repetitive tasks and streamline processes.
Careers in AI
Many people thought that AI is a new industry or job breed. In fact it is not. There are job titles that do not have the word AI in them, but are playing the support role.AI Engineer

AI Engineers are responsible for designing, developing, and deploying AI systems.
They work closely with other engineers and scientists to develop new AI applications and to improve existing ones.
Some of the tasks they do include:
- Designing and developing AI systems
- Testing and debugging AI systems
- Deploying AI systems
- Monitoring and maintaining AI systems
Machine Learning Engineer
 Machine learning (ML) is the core of AI, and it’s the ML engineer who makes the computers really smart.
ML engineers write special programs called “models“.
These models teach the computers how to see (computer vision), how to listen (voice recognition), and how to read (natural language processing).
Then, ML engineers will work with developers to take these models to production for real-life use cases. But their job doesn’t end here. They will need to constantly monitor the metrics and improve their performance.
Companies that hire machine learning engineers: Semiconductor, accounting, healthcare.
Machine learning (ML) is the core of AI, and it’s the ML engineer who makes the computers really smart.
ML engineers write special programs called “models“.
These models teach the computers how to see (computer vision), how to listen (voice recognition), and how to read (natural language processing).
Then, ML engineers will work with developers to take these models to production for real-life use cases. But their job doesn’t end here. They will need to constantly monitor the metrics and improve their performance.
Companies that hire machine learning engineers: Semiconductor, accounting, healthcare.
Besides these two tech jobs, there are other positions that can be redefined to adopt to the changes in the AI era. For example:
AI product manager
In general, a product manager is someone who is in charge of making sure a product is helping users to solve their problems.
Therefore, an AI product manager needs to make sure a product uses AI in an logical way, and doing things that normally only humans can do. For example, understand language or recognize images.
The main job of the AI product manager is to lead the product team and plan how the product will develop.
They decide what features the product needs and how AI can help build those features.
AI product managers also need to make sure the products follow laws and ethics about AI, and the products are fair and safe for people.
Therefore, AI product manager is an exciting role, requires someone who is agile and has genuine interest in using AI to do good.
At the time of writing this (December 2023, there are many people think that prompt engineers will be still in demand.
I personally don’t think so.
I believe the AI will get smarter and smarter in a short period of time, that we do not need a specialist that is trained on how to speak to AI. Any normal people can communicate with AI with no obstacles.
Or rather, AI should be smart enough to tell us there are problems with our prompts.
Challenges that Malaysia Face
Like many other countries, Malaysia face several challenges while rolling out a country wide AI plan.
Education and Skills Training
One of the biggest challenges is to make sure people have the right skills for AI related jobs.
Schools and colleges need to keep up-to-date, and teach subjects like computer science, data analysis, and problem-solving. While meeting the requirements set by Malaysian Qualifications Agency.
We need to also make sure we can attract researchers, scientist, and other experts to come to Malaysia to advance AI development, and retain these talent for long term.
Ultimately, everyone should be savy in AI, but the adoption rate remain unpredictable.
Infrastructure
First, we have a connectivity issue.
While major cities have 5G connectivity, their performance fluctuates and is not stable to provide AI applications that requires high computation power and low latency.
Secondly, the AI legal landscape is still unclear.
For certain regulated industries like banking and insurance, they concern about data privacy, missing AI regulations, and we need a workforce to lead the initiative.
The social and cultural factors add another layer of complexity.
We need a solid plan to upskill existing workers and making sure they are able to transition to the AI and data economy.
A large scale retraining programs is also help to reduce public wariness about job loss, which is one of the major obstacles in AI adoption.
Balancing Traditional Industries
Malaysia has many traditional industries like agriculture and manufacturing.
These industries are due for a tech refresh. It’s to update their existing technologies to get more features, better performance, and improve security.
Introducing AI to these sectors is challenging because it will change how things have been done for a long time. Most of the traditional industry players have a “wait-and-see” mentality.
They will wait for government grants, and observe the big players, before they finally make a move.
Malaysia should invest in specialized datasets and AI models tailored to local markets. This will avoid reliance on Western contexts and boost the competitiveness of core industries in the region.
Partnerships between smaller traditional companies and AI startups can also facilitate technology transfer.
AI Outlooks and Trends in 2024
Wider Adoption
More and more companies will realize that having AI applications is like having a super hero in their team.
But the gap is still there because many companies are not ready, even though they understand the urgency.

99% of Malaysian companies see the urgency, but only 13% are fully ready.
These companies will start to increase their investment in AI and learn how to measure the ROI so that they can tie it to the right KPI.
The AI adoption rate will continue to increase because of the ease of use and the cheaper price.
Prompt Engineering Fades Off
AI is getting smarter at understanding people. Chatbots can now text back and forth, answer questions, and debug codes.
Therefore, the fine line between prompt engineering and human instructions is getting thinner.
Ultimately, even the GPT itself can tell humans that their prompts are not good and teach us how to perfect them.
The voice chat feature of the ChatGPT app is also fluent. We are almost like having a personal assistant in our pocket.
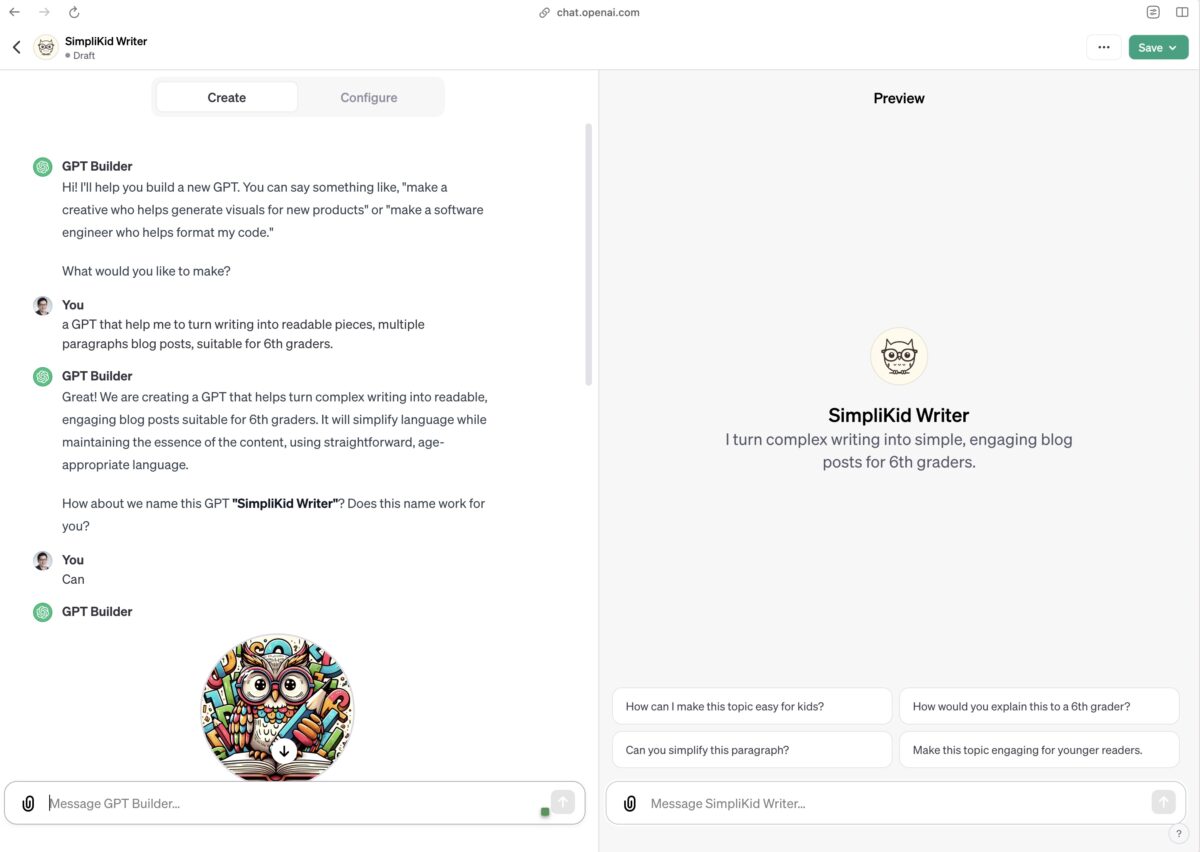
You can create own GPT in less than 5 minutes.
Of course, prompt engineering will not “die off” instantly. There are many situations, like photo generation, where we still need professional prompts to achieve certain styles or effects that we want.
Perhaps a more correct way is to call it “prompting”, which simply means the way we can command AI to do tasks for us using only spoken language.
More government initiatives and AI adoption
AI is the new electricity. Therefore, I expect all industries to do a tech refresh using AI technologies.
Many of the applications are proven in foreign markets. All we have to do is follow their lead and develop similar solutions tailored to the needs of the Malaysian market.
We can also expect further support for AI development and adoption from Malaysian governments.
It can be in the form of initiatives like funding, tax breaks, and talent development programs. Or including AI in the curriculum.
Conclusions
AI in Malaysia is at an important and exciting junction.
The government will continue to help businesses to start using AI more.
Although there are some challenges, like making sure everyone knows how to work with AI and not too worried, things are looking up.
It’s a time for big changes and new ideas in Malaysia with AI. This could lead to better ways of doing things and make Malaysia a key player for AI in the region.
What do you think? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.


0 Comments